
If you look at the head of a stainless steel fastener, you might see a marking stamped onto the surface. These marks hold valuable information about the fastener and learning how to read them can help you decide if it’s the correct product for the job.
In the chart below are the most common head marks found on Anzor's fasteners.
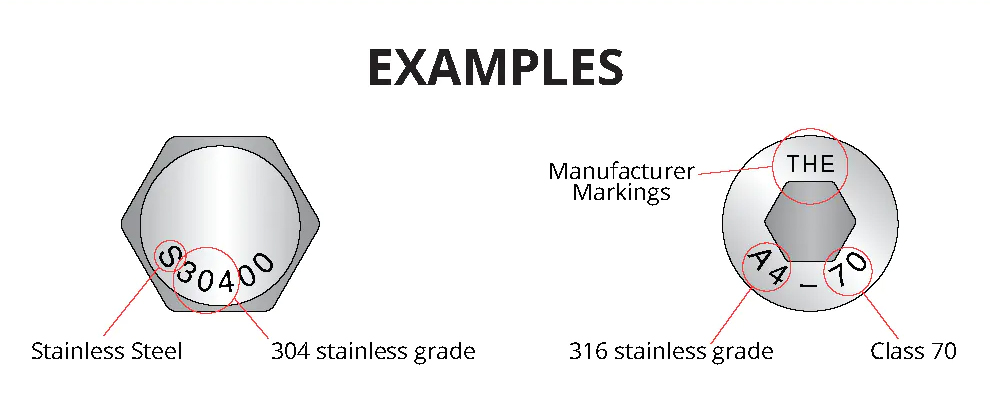
| Markings | What they mean |
|---|---|
| A2 | 304 Stainless |
| A4 | 316 Stainless |
| A2 or A4 with 70 or 80 e.g. A4-80 | Class 70 or 80 (700/800mpa tensile strength) |
| 18-8 | 304 (usually on imperial sized fasteners) |
| 18-10 | 316 (usually on imperial sized fasteners) |
| 304 | 304 SS |
| 316 | 316 SS |
| 316L | 316 SS low carbon |
| Manufacturer markings | e.g THE, Bumax |
| 70 | 700 class Mpa |
| 80 | 800 class Mpa |
No. Austenitic grades of stainless such as 304 and 316 are NOT magnetic in their raw, annealed state.
However when fasteners are manufactured there are processes such as drawing, cold forming and thread rolling which cold-work the material and can magnetize it. This is also the case with lost wax casting of fittings made from molten stainless steel. Therefore some stainless steel fasteners and fittings made of grade 304 and 316 are slightly magnetic, hence using a magnet to determine if it is stainless steel is not a suitable test.

The following types of stainless are typically magnetic in any form:
The following types of stainless are NOT magnetic in their raw, annealed state but can be made magnetic in fastener and fitting manufacturing processes and cold-working:
The head marking 'A2' identifies 304 grad and 'A4' identifies 316 grade. However testing the stainless chemically is the only sure way of knowing the grade.
The only true way to ensure specification compliance is a material elementary analysis with an X-Ray Spectrometer. To be able to be classed as stainless it will have a chemical composition of at least 10.5% Chromium, and meet other requirements depending on what stainless steel grade it should be.
A moly drop test is a chemical test showing the presence of Molybdenum which is present in grade 316 but not 304. However this test is only indicative and will not ensure the material meets the minimum 2% Molybdenum required in the Stainless Grade 316 specification.

Build Your Deck Faster With Our Decking Screw Calculator
Super Duplex 2507 Stainless Steel for Engineering & Manufacturing
To receive useful info and product updates add your details below